What are Cryogenic Temperatures in Welding?
Cryogenic temperatures are extremely low temperatures that are usually associated with liquified gases. The range for cryogenic temperatures is typical -100øF to -400øF. In welding, cryogenic temperatures can be used to cool and solidify metals so that they can be more easily worked with. When metals are cooled to these low temperatures, they become much harder and less malleable, making them easier to shape and work with.
There are a variety of applications for cryogenic temperatures in welding:
- One common use is for hardening metals that are difficult to work with at regular temperatures. By cooling the metal down to a cryogenic temperature, it becomes much harder and less likely to warp or deform during the welding process. This can be especially helpful when welding metals that are thick or have complex shapes.
- Another use for cryogenic temperatures in welding is for repairing damaged metal. When metal is damaged, it can often be difficult to weld it back together using traditional methods. However, by cooling the metal down to a cryogenic temperature, the damage can be repaired much more easily. This is because the metal becomes harder and less brittle at these low temperatures, making it less likely to break or crack during the repair process.
Cryogenic temperatures can also be used to improve the quality of welds. When welds are cooled to cryogenic temperatures, they become stronger and more durable. This is because the metal expands slightly as it cools, which helps to fill in any gaps or irregularities in the weld. This can be especially helpful when welding metals that are thin or have delicate shapes.
How are cryogenic temperatures reached?
There are a few different ways to reach cryogenic temperatures:
- One common method is to use liquid nitrogen. Liquid nitrogen is very cold and can be used to cool metals down to the desired temperature.
- Another common method is to use argon gas. Argon gas is also very cold and can be used to cool metals down to the desired temperature.
What is the purpose of cryogenics?
The purpose of cryogenics is to provide an environment in which metals can be cooled to extremely low temperatures. This can be useful for a variety of reasons, including hardening metals, repairing damage, and improving the quality of welds.
What are the benefits of using cryogenics?
There are several benefits to using cryogenics:
- One benefit is that it can help to harden metals. When metals are cooled to cryogenic temperatures, they become much harder and less malleable. This can be helpful when welding metals that are thick or have complex shapes.
- Another benefit is that it can help to repair damaged metal. When metal is damaged, it can often be difficult to weld it back together using traditional methods. However, by cooling the metal down to a cryogenic temperature, the damage can be repaired much more easily.
- A third benefit is that it can help to improve the quality of welds. When welds are cooled to cryogenic temperatures, they become stronger and more durable. This is because the metal expands slightly as it cools, which helps to fill in any gaps or irregularities in the weld.
What are the disadvantages of using cryogenics?
There are a few disadvantages to using cryogenics:
- One disadvantage is that it can be difficult to reach cryogenic temperatures. There are a few different ways to reach cryogenic temperatures, but it can still be challenging to get the metal down to the desired temperature.
- Another disadvantage is that it can be expensive to use cryogenics. The equipment needed to cool metals down to cryogenic temperatures can be costly, and the process itself can take a long time.
- A third disadvantage is that it can be dangerous to work with cryogenic temperatures. Liquid nitrogen and argon gas are both very cold and can cause serious damage if they come into contact with skin.
It is important to take precautions when working with these materials and to always wear protective clothing.
Cryogenic temperature measurement
There are a few different ways to measure cryogenic temperatures:
- One common method is to use a thermocouple. A thermocouple is a device that measures the temperature of two objects by measuring the voltage between them.
- Another common method is to use an infrared camera. An infrared camera can be used to measure the temperature of an object by detecting the infrared radiation it emits.
- A third method is to use a liquid nitrogen bath. A liquid nitrogen bath is a container filled with liquid nitrogen. The temperature of the metal can be measured by placing it in the bath and measuring the temperature of the liquid nitrogen.
The cryogenic temperature of hydrogen
The cryogenic temperature of hydrogen is -423.17°F.
Related Links
Cryogenics | physics
Cryogenics
Cryogenic Temperature – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Refrigeration Systems for Achieving Cryogenic Temperatures
Cryogenics – Methods Of Producing Cryogenic Temperatures – Liquid, Process, Gas, and Joule – JRank Articles
Related Videos
Cryogenics Working Principle , Animation Importance and Advantageous
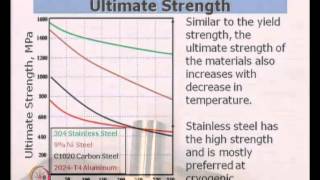
Mod-01 Lec-05 Material Properties at Low Temperature

What Is Cryogenics What Does Cryogenics Mean Cryogenics Meaning, Definition & Explanation
-
Cryogenics Working Principle , Animation Importance and Advantageous
-
Mod-01 Lec-05 Material Properties at Low Temperature
-
What Is Cryogenics What Does Cryogenics Mean Cryogenics Meaning, Definition & Explanation